Dynamic Loading of Message Catalogs
Internationalization in modern applications requires careful handling of localized messages to avoid bloating the initial bundle size. By default, Lingui makes it easy to load all strings for a single active locale. For even greater efficiency, developers can selectively load only the messages needed on demand using i18n.load, ensuring minimal resource usage.
The I18nProvider component doesn't make assumptions about your app's structure, giving you the freedom to load only the necessary messages for the currently selected language.
This guide shows how to set up dynamic loading of message catalogs, ensuring only the needed catalogs are loaded, which reduces bundle size and improves performance.
Final i18n Loader Helper
The following code defines the complete logic for dynamically loading and activating message catalogs based on the selected locale. It ensures that only the required catalog is loaded at runtime, optimizing performance:
import { i18n } from "@lingui/core";
export const locales = {
en: "English",
cs: "Česky",
};
export const defaultLocale = "en";
/**
* We do a dynamic import of just the catalog that we need
* @param locale any locale string
*/
export async function dynamicActivate(locale: string) {
const { messages } = await import(`./locales/${locale}/messages`);
i18n.load(locale, messages);
i18n.activate(locale);
}
Even the "default" locale requires a catalog to be loaded. Lingui aims to keep the internationalization footprint to a minimum by dropping default messages from the production build. This way, only the catalog for the active language is loaded, avoiding duplication.
Without this optimization, switching from the default language (e.g. EN) to another (e.g. FR) would require loading both language catalogs. This strategy ensures efficiency by loading only the necessary messages for one language at a time.
Usage in Your Application
To use the dynamicActivate function in your application, you must call it on application startup. The following example shows how to use it in a React application:
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
import App from "./App";
import { I18nProvider } from "@lingui/react";
import { i18n } from "@lingui/core";
import { defaultLocale, dynamicActivate } from "./i18n";
const I18nApp = () => {
useEffect(() => {
// With this method we dynamically load the catalogs
dynamicActivate(defaultLocale);
}, []);
return (
<I18nProvider i18n={i18n}>
<App />
</I18nProvider>
);
};
Optimized Bundle Structure
Looking at the contents of the build directory, we find a separate chunk for each language:
i18n-0.c433b3bd.chunk.js
i18n-1.f0cf2e3d.chunk.js
main.ab4626ef.js
When the page is first loaded, only the main bundle and the bundle for the first language are loaded:
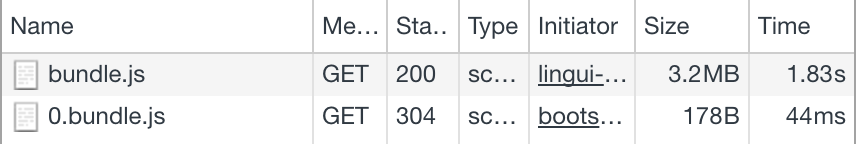
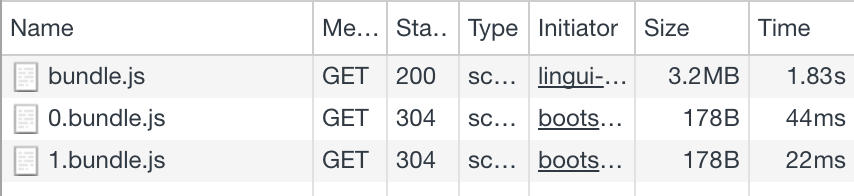
After changing the language in the UI, the second language bundle is loaded:
Dependency Tree Extractor (experimental)
The Dependency Tree Extractor is an experimental feature designed to improve message extraction by analyzing the dependency tree of your application. This tool improves the efficiency of loading localized messages by identifying only the necessary messages for each component or page, rather than extracting all messages into a single catalog.
This allows for a more granular extraction process, resulting in smaller and more relevant message catalogs.
For detailed guidance on message extraction, refer to the Message Extraction guide.